Strategic advice to leverage new technologies
Technology is at the heart of nearly every enterprise, enabling new business models and strategies, and serving as the catalyst to industry convergence. Leveraging the right technology can improve business outcomes, providing intelligence and insights that help you make more informed and accurate decisions. From finding patterns in data through data science, to curating relevant insights with data analytics, to the predictive abilities and innumerable applications of AI, to solving challenging business problems with ML, NLP, and knowledge graphs, technology has brought decision-making to a more intelligent level. Keep pace with the technology trends, opportunities, applications, and real-world use cases that will move your organization closer to its transformation and business goals.
Recently Published
Automobile insurers have been capturing and analyzing data from sensor devices deployed in their customers' vehicles for some time. And the availability of such usage-based insurance (UBI) programs has grown considerably as insurance companies have expanded their in-vehicle offerings to various consumer groups (commuters, new drivers, etc.) and to commercial fleet operators.
This Executive Report examines the transformation taking place in healthcare, research, and medicine -- including key trends and developments around the application of mobile connected devices combined with cloud and big data analysis technologies applied to healthcare, fitness, and wellness programs. It also considers the benefits and issues involved in using sensor and other data acquired from personal mobile devices in conjunction with other forms of medical and healthcare data.
The growing use of personal fitness trackers, smart watches, connected medical devices, and a myriad of sensor-enabled apps running on smartphones is also generating vast amounts of health data about consumers. For the most part, this data has not been used to any real extent by healthcare providers, clinicians, and researchers to promote the overall health and well being of patients and consumers. This is changing, and we are seeing a revolution in healthcare with the application of mHealth ("mobile health") technologies and practices.
The distinctive features of cloud computing offer many potential opportunities for business innovation, particularly given its service (and service quality) focus, coupled with the flexibility that new technology delivery mechanisms provide. However, our most recent research finds good reasons for qualifying the assumption of frictionless innovation arising from cloud adoption. The pattern, instead, may well follow past diffusions of other potentially powerful technological innovations, including the Internet itself.
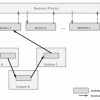
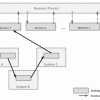
A Service Assurance Architecture Pattern
To be faster and cheaper, DevOps should integrate currently separated QA tasks -- from testing done during development to monitoring executed on daily operations routines -- under a common, business-oriented, and actionable QA architecture, designed and built into IT systems. This Executive Report offers such an architecture pattern for IT service assurance.
A Service Assurance Architecture Pattern (Executive Summary)
The latest trends, including DevOps, prove that we must extend quality assurance (QA) efforts to the operations and maintenance period, and we must focus them on the services provided by IT. QA work also involves the amount of time and money spent, right? Not necessarily.
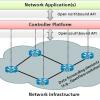
Software-Defined Networks
Traditional computer networks are complex and very hard to manage (see "Unraveling the Complexity of Network Management"). To express the desired policies, network operators need to configure each individual network device, one by one, either manually or with the use of low-level scripts. In addition to configuration complexity, network environments have to endure the dynamics of faults and adapt to load changes. Enforcing the required policies in such a dynamic environment is highly challenging.
In this Executive Report, Part II of a series on cloud computing, we explore the effective adoption and management of the cloud by small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) as well as global leading firms. Using case examples, we demonstrate, in detail, the challenges and practices used with these types of organizations. We also provide three distinctive lessons for SMEs and 10 lessons for all organizations.