Strategic advice to leverage new technologies
Technology is at the heart of nearly every enterprise, enabling new business models and strategies, and serving as the catalyst to industry convergence. Leveraging the right technology can improve business outcomes, providing intelligence and insights that help you make more informed and accurate decisions. From finding patterns in data through data science, to curating relevant insights with data analytics, to the predictive abilities and innumerable applications of AI, to solving challenging business problems with ML, NLP, and knowledge graphs, technology has brought decision-making to a more intelligent level. Keep pace with the technology trends, opportunities, applications, and real-world use cases that will move your organization closer to its transformation and business goals.
Recently Published
Data is now recognized as the heart of every organization. No longer limited to retrospective analysis, it can be applied for predictive, strategic purposes as well as empower new capabilities.
Smart clothing utilizes textile sensors embedded directly within their fabrics. This allows such garments to function as biometric data-gathering devices. Examples include shirts, sports bras, gloves, smart socks, and shoes that can capture and relay information from the wearer -- such as heart rate, perspiration, respiration, grip, running form, fitness levels, and more. The data is typically transmitted wirelessly to a smartphone to provide direct feedback to the wearer, and to a cloud platform for applying machine learning (ML) and other analytics in order to generate behavioral feedback.
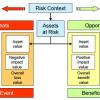
SABSA Framework: An Overview
This Executive Update offers an overview of the Sherwood Applied Business Security Architecture (SABSA) — a free-use, open source security architecture framework that is particularly useful for enterprise architects.
Smart Manufacturing: The Fourth Industrial Revolution?
This Executive Update provides an understanding of the concepts behind fork and pull and its possible applications for internal and external software development projects, as well as its potential for other applications.
Development and operations groups play equally important roles and must synchronize their work to enable organizations to rapidly produce software products and services. The awareness of this has resulted in the development of the operating principles known as "DevOps."
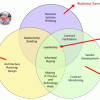
Enterprises, under constant pressure to marshal finite resources, are understandably selective about investments, and must choose wisely between candidate investments with different rewards and unequal risk profiles. This Advisor starts from the position that architecture too should be viewed as an organizational investment, and responsibly managed as one. To be able to do that effectively, we need to get our arms around the value of architecture.
I know of several projects under way utilizing sensors, analytics, and mobile technologies to optimize rail operations by collecting and analyzing operational data to determine real-time vehicle location and operating factors such as average acceleration, speed, idle times, number of stops, driver performance, and so on, and to assess KPIs on equipment wear and rail/roadbed conditions.
This Executive Report details seven major challenges experienced when adopting the cloud. The technology function requires new, turbo-charged core capabilities in business innovation, business savvy, governance, architecting, and specialist sourcing as an "anchor" policy for moving to the cloud.