CUTTER BUSINESS TECHNOLOGY JOURNAL VOL. 30, NO. 3
Welcome to the Digital Age
We are living in the digital age, where emerging digital technologies, business models, and the reduced cost and time for trying out innovative business solutions are transforming both personal behaviors and businesses, irrespective of a company’s industry, geography, or size. Attend any conference or open any magazine, and chances are you will be reminded about the need to exploit the new business opportunities created by the ongoing digital disruption or run the risk of being left behind. Business leaders need to be aware of the risks posed by agile, innovative firms that can respond faster to dynamic business demands, provide timely competitive offerings, and deliver enhanced customer experience while reinventing — or at times newly inventing — sectors of the economy.
No industry is immune to digital disruption, and most of them are in varying stages of responding to the phenomenon in the hope of retaining — and hopefully growing — their market share. Successful digital startups like Uber (taxi, shared economy), Netflix (movie and TV show rental/streaming), Amazon (retail and cloud services), Facebook (social), and Airbnb (hospitality) are perfect examples of disruptors that, in a very short period of time, have established themselves as leaders of their respective business domains while offering tough competition to market leaders and at times driving them out of business. As of last year, five of the top seven S&P 500 companies (Apple, Alphabet, Microsoft, Amazon, and Facebook) were businesses that were started within the past three decades with small seed money but big, innovative ideas that led either to reinventing a market or creating a new one.
Today’s pure digital businesses (e.g., Amazon, Facebook, Google) serve as role models for savvy traditional companies (e.g., GM, Citi) that are ready to retool and advance into the digital age. A quick review of companies listed in the Fortune 100 over a period of a few decades shows that remaining on this list is tough; it requires ongoing innovation, agility, and capability to adapt to a dynamic business environment. Established companies like GE, Disney, JPMorgan Chase, and American Airlines have proved that being innovative and agile is not limited to startups. These companies are successfully executing on their own digital transformation journey while taking full advantage of opportunities provided by digital disruption.
In this article, I discuss key drivers for adoption of digital business, propose a framework organizations can use to guide their digital transformation efforts, and consider the value digital transformation is delivering in areas of healthcare, travel, and government.
Drivers of Digital Business
Digital experiences have become a standard part of daily life. Leading companies recognize that digital disruption presents multiple growth opportunities, including delighting their customers with convenience and personalization, leveraging the wealth of data trails from digital activity to get even closer to the customer, and using technology to operate faster and better.
The digital business trend is driven by many factors, including technological advances, emerging business models, increasing customer expectations, and the will to retain market leadership. Disruptive innovations are interrupting businesses continuously in almost every sector, and everyone seems to be in a race to become the leader of their own industry.
Figure 1 provides a quick overview of the leading drivers influencing the next wave of innovation and digital businesses. To be successful with digital transformation, organizations need to understand these drivers properly and develop and execute on a holistic, integrated strategic plan addressing the needs of the business.
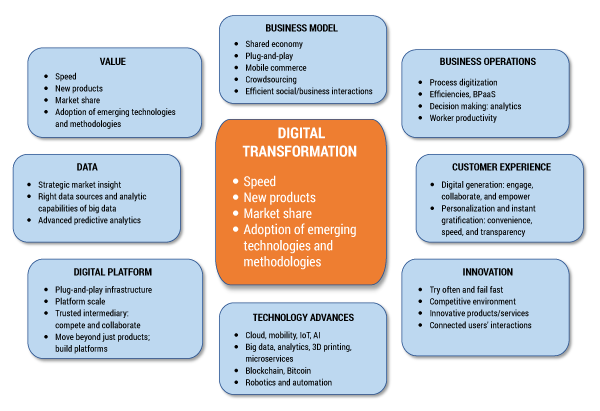
Figure 1 — Key drivers impacting businesses and encouraging digital transformation.
Technology Advances
Over the past couple of decades, technologies have advanced and become ready for industrial use at an unprecedented rate, impacting all aspects of business. Organizations are actively considering technologies like artificial intelligence (AI), the Internet of Things (IoT), cloud, 3D printing, predictive analytics, computer vision, and others for the solutions they are envisioning. For example, smart cities solutions rely on IoT, analytics, and AI; self-driving cars leverage sensors, computer vision, robotics, and AI; and digital healthcare and artificial limbs depend heavily on AI, analytics, and 3D and 4D printers. Leveraging these technology advances requires an integrated, holistic plan to achieve optimal benefits.
We’re now in the midst of an ongoing emergence of revolutionary technologies such as blockchain, Bitcoin, microservices, APIs, and so on, each one quite capable of transforming an existing industry or creating a new one. Consider blockchain, which is an open distributed ledger that can record transactions between two parties efficiently and in a verifiable and permanent way. The ledger itself can also be programmed to trigger transactions automatically. Over half of respondents to a recent Cutter survey are exploring blockchain to exploit its financial transaction management capabilities. According to another industry survey, 90% of major banks in North America are exploring the use of blockchain technology for payments. One accounting firm, EY Switzerland, has provided digital wallets to all of its employees, has installed a Bitcoin ATM in its office in Zurich, and accepts Bitcoin as payment for all its consulting services. Companies such as Netflix believe that speed is key to winning in the marketplace and are adopting technologies like microservices, APIs, and DevOps to achieve the required speed and replace silos with microservices teams.
Business Model
With these technology advances, new business models such as shared services (e.g., Uber, Airbnb), mobile banking (e.g., payments, funds transfers, remote deposits), and crowdsourcing (e.g., Be My Eyes, IdeaConnection) have matured and become viable. Other disruptive business models include:
- App-only banks with no branch offices but higher returns
- Healthcare plans that use high-tech screening and wellness tools to deliver health services for US $149/month with no limits or deductibles
- Robots that can “walk” a farmer’s crops looking for pests
- Digital government initiatives that use emerging technologies to improve citizen services
The advent of new business models and supporting technologies has opened new business opportunities that individuals and companies — from startups to large established firms — can pursue. Companies are not only reengineering and optimizing their business processes to leverage new technologies, they are also transforming how these processes interact with each other within the company and between involved partners.
Business Operations
Customer experience is arguably the first change observers will notice as a result of digital transformation, but it is just one part of digital transformation, albeit a highly visible one. Other parts of the transformation are generally hidden behind the scenes, but they are as critical as customer experience. Businesses are getting big paybacks from digitization of internal processes, which enhances employee productivity and overall performance. Leveraging automation and process digitization enables the delivery of business processes as a service (BPaaS), as well as self-service for standard functions like HR-related tasks. Collaborative tools allow for virtual teams, thereby removing the limitation of physical offices and facilitating more active participation by all. These capabilities are critical for the bottom line in terms of overall speed, throughput, profit, company reputation, and growing revenue from digital business.
Digital Platform
With digital business, the distinction between partners and rivals is being blurred, and businesses need to develop a keen understanding of all the different relationships that might exist between firms in their orbit and how they might cooperate and/or compete with them. It is quite possible to compete with a company for one business opportunity while cooperating with them on another, resulting in what has been called “coopetition.” For example, within the entertainment (television) industry, HBO competes with Netflix (as it does with Showtime) for programming market share, but it collaborates with Netflix to have leverage against distribution channels such as Comcast and Amazon.
Firms should focus on developing effective digital platforms and becoming trusted intermediaries that can bring competing businesses together. Some fast-growing companies like Facebook, Apple, Uber, and Airbnb are leveraging digital platforms for business growth. These businesses have created an open, participative, plug-and-play infrastructure that allows both consumers and producers to collaborate and work together effectively, enhancing overall business value.
Data Analytics
In today’s digital world, it is critical to assemble the right data and turn it into strategic assets to make timely decisions for business and customer interactions. Most probably, this will require collaboration not just within an organization but with partners as well. As part of a data strategy, we need to consider data sources, analytical capabilities of big data, the role of data-driven decision making, and risks around data privacy and security.
Customer Experience
We are living in an experience-based economy without traditional loyalty to brand or company. Irrespective of industry, one common competitive advantage is the customer experience you offer. A high level of differentiated experience enables market leadership (think Amazon in retail, or Netflix in entertainment) and a premium price position. Providing a great customer experience requires a good understanding of your customers and the digitization of customer touchpoints.
Businesses are building their analytics capability to understand customers in more detail. For example, insurance companies are improving their portfolios and cost structures through analytics-based underwriting and pricing and using technology to enhance in-person sales conversations.
Innovation
Today’s emerging companies are born digital. They can change — and change fast — to answer consumer demand or a competitive offering. So how can an enterprise win at digital? I believe the answer lies in digital transformation and the innovative solutions you develop as part of it.
A Digital Transformation Framework
An effective transformation framework and plan can support enterprises in achieving their full potential in the age of disruption. In my view, there are three approaches to digital transformation:
- Business model transformation
- Business operations transformation
- IT transformation
These approaches are well integrated with each other, and organizations need to look at them in a holistic manner instead of treating them in isolation. Figure 2 provides a high-level overview of a digital transformation framework that has been used successfully by many businesses across different industries.
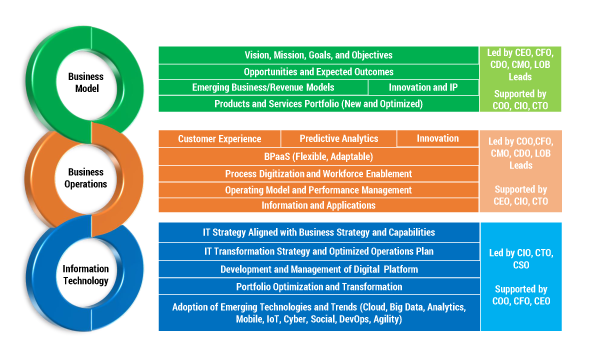
Figure 2 — A digital transformation framework.
Business Model Transformation
The rarest and least predictable of the digital transformation approaches, business model transformation causes the most disruption not only to the business itself, but at times to the whole ecosystem in which a business exists. It typically involves changing part of the supply chain and thus impacts both operations and the underlying IT. This approach is generally led by the CEO, CFO, or CMO and is supported by the COO, CIO, CTO, and other business leaders. Businesses that rely heavily on data intelligence need to develop connected services and produce insights to see what can be monetized to unlock new business models.
Business Operations Transformation
Digital technologies allow businesses to move at incredible speed, accelerating their responsiveness to uncover issues and inefficiencies, predict what will happen, and then adjust as needed. Business operations transformation may be required to support a change in the business model, add a new business capability, or improve operations through the transformation of customer experience, products and services, and/or core operations. One example is using automation to eliminate manual work.
IT Transformation
An organization’s underlying technology will need to transform internally to support new business capabilities, enable operational improvements, and take advantage of emerging technologies like cloud, SaaS, and virtualization. IT transformation requires taking a portfolio approach to IT and managing it effectively to maximize the return on investment while meeting business needs. Successful transformation demands an effective alignment of business strategy with IT strategy and the transformation roadmap. While consumers are not aware of the transformation at this level, they will ultimately benefit from it.
Which Approach Should You Choose?
Most enterprises should focus their energies and budget on the sweet spot where they can get quick and long-term benefits — and this may vary depending on their strengths, weaknesses, and competitive pressures. As you start your journey of digital transformation, irrespective of your current situation, keep the following in mind:
- Don’t be hyperactive; think rationally about your fear and anxiety.
- The best response to fight back against disruption is not to try to replicate the disruptor’s strategy and look to disrupt a business model, but instead to focus on your products, services, operations, and customer experience.
- Reassess what you do and how you do it. Learn from others who have been disrupted, such as the newspaper and travel industries.
- Customers are focused on features like customer experience and personalization and will move somewhere else if you don’t remove friction from your processes.
Businesses going through digital disruption must ask critical questions about their organization and honestly assess their capabilities to develop a practical strategic plan and move forward to achieve their vision:
- Are we the innovator and disruptor?
- Are we being disrupted by someone else? If so, how: business model, business operations, or IT?
- What are the opportunities and risks posed by digital disruption?
- How do we leverage these opportunities to achieve our full potential and win in the digital age?
- Do we have the right resources and transformation strategy to achieve our vision?
- How do we address the gaps we might have in our strategic plan?
Emerging Digital Business Opportunities and Value
According to industry analysts, 67% of Global 2000 enterprises “will have digital transformation at the center of their corporate strategy” by 2018. Companies like Uber, Netflix, Amazon, Spotify, Coursera, and PayPal started as digital businesses and have digital in their DNA. Many established businesses like Mercedes-Benz, American Airlines, GE, JPMorgan Chase, Boeing, and Walt Disney have made digital transformation a central focus of their business strategy and are reaping the benefits from it. Many other businesses are either in the early stages of this digital transformation or face the risk of becoming obsolete.
Sooner or later, all industries will be impacted by digital disruption. In fact, digital business has invented new industries that did not exist before. Figure 3 provides a quick overview of various industries and their current status in terms of digital disruption.
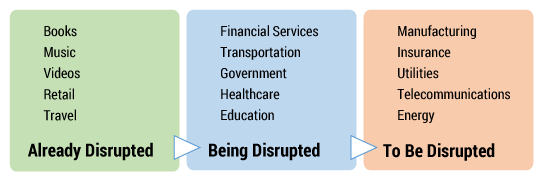
Figure 3 — Industries being impacted by digital disruption.
Even though being disrupted will be difficult on laggards, it does not mean that an industry is dead. It only means that the industry is reinventing itself, and surviving in this environment will require businesses to adapt to the changes quickly. For example, even though many long-standing daily newspapers have withered or died, newspapers like the Washington Post have reinvested in themselves and are beginning to thrive. Depending on the industry, changes may involve new business offerings, new partnership or compensation models, more efficient operations to attract new clients, or improved underlying technologies and infrastructure. For example, within manufacturing, 3D printing may be used to create custom-made parts faster and at a reduced cost. In the following sections, I review three business areas — digital health, digital airline, and digital government — and discuss the currrent state of each industry, key challenges, and the digital disruption taking place. I also show how innovators are converting these challenges into business opportunities and delivering innovative solutions for the benefit of society.
Digital Health
The healthcare industry is under tremendous pressure to deliver higher-quality care at lower cost. Lack of sufficient health insurance, ineffective government policies, and hard-to-access health record data lead to delayed treatment of diseases, increased complexity, and higher cost of treatment. A shortage of skilled healthcare professionals, the emergence of new diseases, and changing expectations from patients make it still more difficult. Going digital is one key to reducing cost by streamlining organizational processes, analyzing the clinical data needed to make better healthcare decisions, and offering better health management tools to caregivers and consumers.
Scores of health providers, both startups and established players, are trying new approaches that use emerging technologies to deliver healthcare services more effectively, often with a focus on prevention, wellness, and managing chronic conditions. Innovators and early adopters of digital health are relying on emerging technologies (cloud, AI, analytics, social, cyber), reengineering patient experience and operations (comprehensive patient engagement, personalized medicine, coordinated care, and record keeping), and focusing on delivering innovative solutions to earn a share of the trillions of dollars in annual healthcare spending. Figure 4 provides details on some of the key capabilities required to achieve the full benefit of digital healthcare.
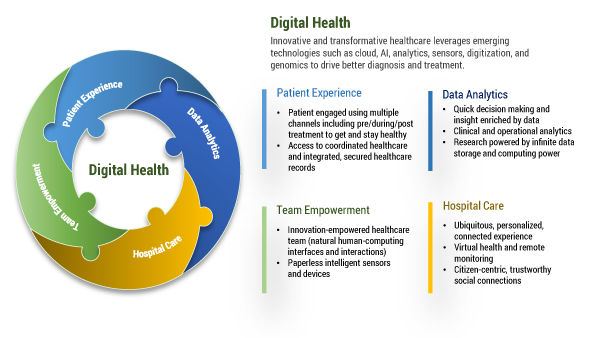
Figure 4 — Essentials for digital health.
Forward, a medical startup just launched by serial entrepreneur Adrian Aoun, provides access to futuristic primary care for US $149 a month. There are no copays, and membership — as with Netflix — covers an all-you-can-consume set of services from the practice: doctor visits, a baseline screening, access to Forward’s team of doctors and nurses via email, ongoing monitoring through wearable devices, and even some medications and supplements. You’ll still need to buy insurance to cover things like hospitalizations, surgeries, and specialist care, but Forward takes care of basic healthcare at a much more reasonable cost.
Digital Airline
Over the past couple of decades, the airline industry has gone through a lot — terrorism, which resulted in increased security requirements and cost; global financial instability, which led to fluctuating travel demand; and higher fuel prices, which impacted the bottom line. Ever-increasing competition from global and regional airlines and travelers’ demands for better customer experience have forced airlines to develop new business models, optimize business operations, and fully leverage emerging technologies effectively.
Digital disruption is impacting all core capabilities of the airline industry, including sales, route scheduling, customer service, seat occupancy, loyalty programs, and more. Airlines that have not been able to change with the times have either been acquired by other airlines or gone out of business. Most airlines that are undergoing digital transformation are focusing on three areas (see Figure 5):
- Customer experience
- Operations and employee productivity
- Aircraft connectivity
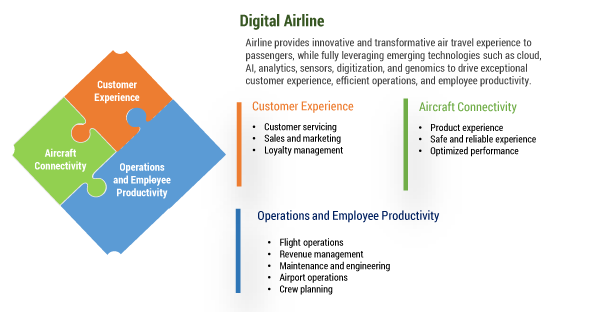
Figure 5 — Essentials for a digital airline.
Customer Experience
Customer experience includes collecting and understanding customer behaviors and providing offers and experiences that are personal, relevant, and connected across all journey touchpoints, thus promoting customer loyalty and workforce productivity. Let us review a couple of these touchpoints:
- Digital airport — provides a seamless transition from arrival at the airport to ticketing to boarding, and then from landing to baggage claim to departure from the airport with personalized and location-aware mobile devices
- Multichannel commerce — focuses on delivering the right product to the right customer in the right place at the right time
Most successful airlines have been focusing on customer experience, and based on an industry poll, JetBlue and Southwest have emerged as the top scoring airlines in this category.
Operations and Employee Productivity
This area includes providing passengers with exceptional integrated services while improving operational efficiencies and capturing critical data in time to provide rich insight. Operational efficiencies include things like efficient flight, ground, and airport operations:
- Flight operations — requires effective communication among crew and maintenance crew to deliver excellent passenger services and resolve issues in time; enables easy access to crew schedule, flight manuals
- Ground operations — enables improved aircraft maintenance and safety through collaboration; quick identification and resolution of any maintenance issues
- Airport operations — leverages in-air and on-ground data and analytics to drive efficiency and resolve any airport operational issues by communicating with experts
Aircraft Connectivity
Seamless connectivity between aircraft, staff, passengers, and processes enables a friction-free passenger journey. It ensures optimal product experience and performance, including onboard comforts and conveniences provided through optimized crew and flight operations.
Digital Government
As private businesses across different industries are transforming themselves with digital technologies, citizens across the globe are calling on their respective governments to follow suit. Even though effecting any change, including digital transformation, tends to be more challenging within the public sector than the private sector, government leaders at all levels are listening to citizens and realizing that they need to transform how government is working today. They are looking for ways to improve the public’s experience with government at the federal, state, local, agency, and department levels and supporting initiatives to build, buy, and share technology that allows for efficient services for citizens and businesses. Constrained budgets and increased expectations from citizens are encouraging the use of emerging digital technologies to reengineer and streamline business processes and operations to deliver services focused on customer experience.
Irrespective of size, the digitizing of any agency is complex and requires special attention to core capabilities for engaging citizens, other agencies, and private businesses. Leading business strategy consulting firms suggest that when done successfully, worldwide government digitization can save $1 trillion annually in economic value. Figure 6 provides a high-level overview of various capabilities a successful digital government must have, as well as some of the critical elements (e.g., strategy, governance) that enable them.
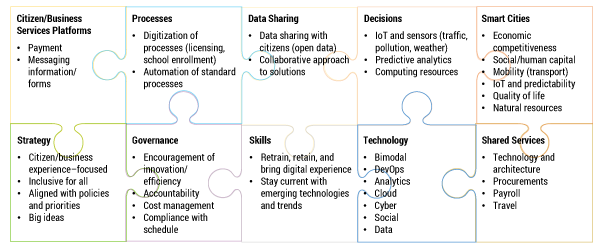
Figure 6 — Essentials for digital government.
Most governments across the globe realize the complexity and criticality of transforming themselves, but they also see the potential benefits of doing so. Examples of digital transformation at the federal and municipal levels include:
- The US General Services Administration (GSA) created 18F (now part of the GSA’s Technology Transformation Service [TTS]) and the White House launched the US Digital Service (USDS) to focus on fostering digital transformation by helping agency leaders understand and implement new approaches, business models, and technologies.
- Striving to become “The Smartest City” in the world, “Singapore is using data to redefine what it means to be a 21st-century metropolis.”
- In India’s Smart Cities Mission, the Ministry of Urban Development has identified 60 cities to be developed as smart cities and “use technology, information, and data to improve infrastructure and services.... [to] improve quality of life, create employment, and enhance incomes for all.”
Digitization helps governments make their services more accessible, efficient, and effective.
Conclusion
The digital age is here to stay, and so are the disruptions it is causing across different industries. In fact, digital transformation is just getting started, with organizations leveraging current and emerging technologies to create new business models and optimize business operations. Successful digital transformation requires organizations to have a holistic view of business strategy that drives overall IT strategy and enables the changes required by business. Even though it is difficult to forecast how much digital disruption will impact any particular industry or business, sooner or later every industry will be affected. Savvy business leaders are not taking any chances and are facing the challenge head on. They are anticipating upcoming digital disruptions and working to convert them into strategic opportunities to retain or gain market leadership. A final word to the wise: be the disruptor or be ready to be disrupted by one.